
Author level metrics provide a measure of impact of one particular author. Most author level metrics incorporate citation counts of articles written.
Example of a Google Scholar Citations Profile
The h-index is a measure of an author's research impact. It is a combined measure of both the productivity (number of papers) and the impact of a researcher’s publications (citations). It provides a mechanism for the work of individual researchers to be compared with others in the same discipline.
Example: If a researcher has an h-index of 4, this means that the researcher has four papers that have each been cited four times or more.
Example: If a researcher has an h-index of 15, the researcher has fifteen papers that have each been cited fifteen times or more.
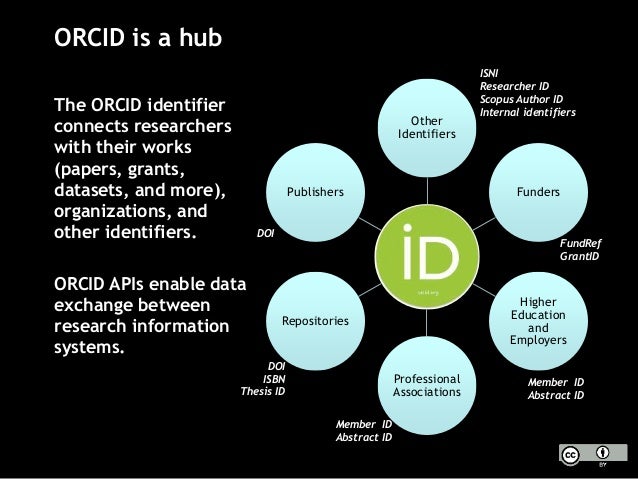
Author identifiers, such as ORCIDs, give you a way to reliably and unambiguously connect your names(s) with your work throughout your career, including your papers, data, biographical information, etc. This can be helpful in a number of ways:
| Product | Type | Registration | Scope/Limitations |
| Open Identifiers | |||
| ISNI (International Standard Name Identifier) |
From ISNI International Agency; ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certified | ISNI gets data from many sources. Search existing IDs on the search page. Apply for an ISNI. |
|
| Proprietary Identifiers | |||
|
Proprietary - From Thomson Reuters |
Fill out the web form, then you'll get an email registration to obtain an ID. |
|
|
| Scopus Author Identifier | From Elsevier | Identifier automatically assigned to all authors indexed in Scopus |
|
| Google Scholar Citations | From Google |
From Google Scholar click My Citations and login to your Google account. After entering information into your profile Google will retrieve articles likely to be authored by you. Articles can then be added to your profile (in groups and/or individually.) |
|
| Repository Identifier | |||
| arXiv Author IDs | From arXiv |
Used to accurately identify contributors to arXiv, an electronic archive of research articles in the sciences maintained by the Cornell University Library. arXiv authors opt-in to create an author ID on the create an author identifier page. |
|
| 500 W. University Avenue : El Paso, TX, 79968-0582 : (915) 747-5672 |